Firewall
Barsukov Vyacheslav Sergeevich,
Candidate of Technical Sciences
FIREWALLS ARE COLLECTING THE RUSSIAN MARKET
With the development of market relations, information is increasingly acquiring the quality of a commodity, that is, it can be bought, sold, transferred and, unfortunately, stolen.
Therefore, the problem of ensuring information security is becoming more and more urgent every year.
One of the possible ways to solve this problem is the use of firewalls.
The article, based on an analysis of the Russian market, discusses the features and possibilities of using the currently most effective and a dynamically developing means of network protection — firewalls.
Modern network protection technologies are one of the most dynamic segments of the modern security market.
Network protection means are developing so rapidly that currently generally accepted terminology in this direction has not yet been fully established.
These means of protection appear in literature and the media as firewalls, firewalls and even information membranes.
But the term “firewalls” (FW) is most often used.
In general, to ensure network protection between two sets of information systems (IS), a screen or information membrane, which is a means of delimiting access of clients from one set of systems to information stored on servers in another set.
In this sense, ME can be represented as a set of filters that analyze what passes through them information and decision makers: skip the information or block it.
At the same time, events are recorded and an alarm is generated if a threat is detected.
Typically, shielding systems are made asymmetrical.
For shields, the concepts of “inside” and “outside” are defined, and the task of the screen is to protect the internal network from a potentially hostile environment.
In addition, ME can be used as a corporate open part of the network, visible from the Internet.
For example, in many organizations MEs are used to store open access data, such as information about products and services, files from databases FTP, error messages and so on.
Modern requirements for firewalls
- The main requirement is to ensure the security of the internal (protected) network and full control over external connections and communication sessions.
- The security system must have powerful and flexible controls to easily and fully implement the organization's security policy.
- The firewall must operate unnoticed by users of the local network and not make it difficult for them to perform legal actions.
- The firewall processor must be fast, work quite efficiently and be able to process all incoming and outgoing traffic in peak modes so that it cannot be processed block a large number of calls and disrupt its operation.
- The security system itself must be reliably protected from any unauthorized influences, since it is the key to confidential information in the organization.
- The firewall management system must be able to centrally ensure the implementation of a unified security policy for remote branches.
- The firewall must have a means of authorizing user access through external connections, which is necessary when employees of the organization work on business trips.
Classification of analyzed firewalls
As is known, to conduct a comparative analysis it is necessary, first of all, to classify the tools being analyzed.
Since firewalls are focused on protecting information in open networks such as the Internet/Intranet, the basis of the approach is the seven-layer ISO/OSI (International standardization organizations).
In accordance with this model, MEs are classified according to the level at which filtering is performed: channel, network, transport, session or application.
Therefore, we can talk about shielding concentrators (link layer), routers(network layer), transport shielding (transport layer), session layer gateways (session layer) and application shields (application layer). p>
It should be noted that at present, along with single-level firewalls, comprehensivescreens are becoming increasingly popular, covering levels from network to application, since such products combine the best properties of single-level firewalls of different types .
Diagram 1 shows the structure of information shielding between two systems using the ISO/OSI reference model.
Features of modern internetworking screens
The results of a more detailed comparative analysis of various types of firewalls are given in table. 1.
Table 1 Features of firewalls
|
Firewall type |
Operation principle |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Screening routers (packet filtering firewalls) | Packet filtering is carried out in accordance with the IP header of the packet according to the criterion: what is not explicitly prohibited is allowed. The information analyzed is: — sender's address; — recipient's address; — application or protocol information; — source port number; — destination port number. |
· Low cost · Minimal impact on network performance · Easy configuration and installation · Transparency to software |
· Vulnerability of the protection mechanism to various types of network attacks, such as spoofing of packet source addresses, unauthorized modification of packet contents · Absence in a number of products supporting event logging and audit tools |
| Screening gateway (ESG) | Information exchange occurs through bastion host, installed between the internal and external networks, which makes decisions about the possibility of routing traffic. There are two types of ES: session and application level | · No end-to-end transmission of packets in case of failures · Strengthened protection mechanisms compared to EM, allowing the use of additional authentication tools, both software and hardware · Using the address translation procedure, which allows hiding the addresses of hosts in a closed network |
· Use of only powerful bastion hosts due to the large volume of calculations · Lack of “transparency” due to the fact that ES introduce delays in the transmission process and require authentication procedures from the user |
| Screening subnets (ES) | An isolated subnet is created between the internal and public networks. Messages from the open network are processed by the application gateway and end up in the electronic signature. After successfully passing control at the electronic signature, they enter a closed network. Requests from a closed network are processed through the electronic signature in the same way. Filtering is carried out according to the principle: what is not allowed is prohibited | · Possibility of hiding the internal network address · Increased security reliability · Possibility of creating large traffic between internal and open networks when using several bastion hosts in ES · “transparency” of work for any network services and any internal network structure |
· Using only powerful bastion hosts due to the large amount of computation · Maintenance (installation, configuration) can only be carried out by specialists |
As can be seen from Table 1, a firewall is the most common means of enhancing traditional means of protection against unauthorized access and is used to ensure data protection when organizing internetwork communication.
Specific firewall implementations largely depend on the computing platforms used, but , however, all systems of this class use two mechanisms, one of which ensures blocking of network traffic, and the second, on the contrary, allows data exchange.
At the same time, some versions of ME focus on blocking unwanted traffic, and others focus on regulating permitted machine-to-machine exchange.
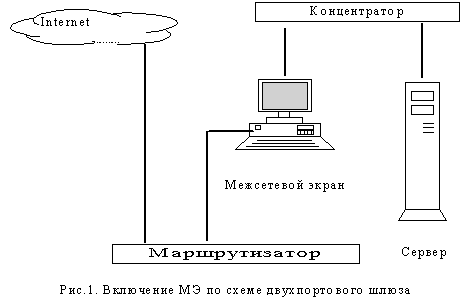
Typical options for enabling firewalls
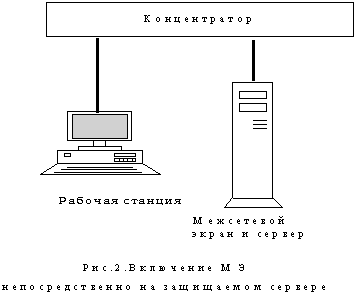
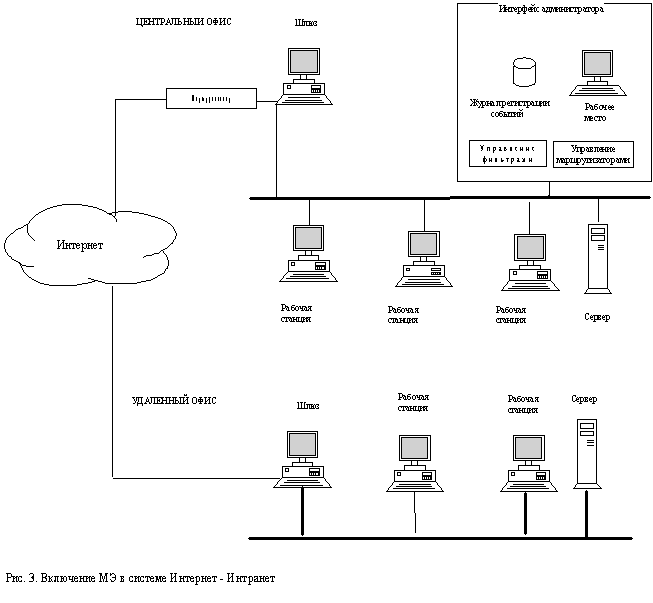
Comparative characteristics of modern firewalls
Based on the results of the analysis of the Russian market, Table 2 shows the comparative characteristics of modern firewalls.
Table 2. Comparative characteristics of modern firewalls
| Product | Type | Platform | Company | Features |
| Solstice Firewall — 1 | Complex screen | SunOS, UNIX, Solaris | Sun Microsystems | Implements security policy: all data, without explicit permission — are discarded. During operation, packet filters on gateways and servers generate records of all events and trigger alarm mechanisms that require administrator response. |
| Black Hole | Application layer shield gateway | Various hardware platforms | Milkyway Networks Corporation | Does not use a packet filtering mechanism. Operating principle: that which is not expressly permitted is prohibited. Registers all server actions and warns of possible violations. Can be used as a bidirectional gateway. |
| BorderWare Firewall Server | Application level shielding gateway | UNIX, Windows, DOS | Secure Computing Corporation | Software protection tool that ensures operation under OS control (our own development). Allows you to record addresses, time, attempts, protocol used. |
| ALF (Application Layer Filter) | Application layer shielding gateway | BSDI | SOS Corporation | Can filter IP packets by addresses, port ranges, protocols and interfaces. An incoming packet can be skipped, discarded, or sent to its address. |
| ANS InterLock Service | Application layer shielding gateway | UNIX | ANS CO + RE Systems | Uses intermediary programs for Telnet, FTR, HTTR services. Supports encryption of point-to-point connections, and hardware can be used as authentication means. |
| Brimstone | Integrated screen | SunOS, BSDI on Intel, IRIX on INDY and Challenge | SOS Corporation | Uses time, date, address, port, etc. for analysis. Includes application layer proxies for Telnet, FTR, SMTP, X11, HTTP, Gopher, and more. Supports most hardware authentication packages. |
| Centri | Application layer shielding gateway | SunOS, BSDI, Solaris, HP-UX, AIX | Global Internet | A closed network is seen from the outside as a single host. Has intermediary programs for services: email, FTR protocol, etc. Registers all server actions, warns of violations. |
| CONNECT | Application layer shielding gateway | UNIX | Sterling Software | It is a software product that protects information from unauthorized access when connecting closed and open networks. Allows you to record all server actions and warn about possible violations. |
| CyberGuard Firewall | Bidirectional gateway of complex type (host-bastion as a filter, application level gateway or complex screen) | RISC platform, OS UNIX | Harris Computer Systems Corporation | Complex solutions were used, including UNIX OS security mechanisms and integrated network tools designed for RISC computers. The source address, destination address, etc. are used for analysis. |
| Digital Firewall for UNIX | Integrated Screen | Digital Alpha | Digital Equipment Corporation | Pre-installed on Digital Alpha systems and providing shielding filter and application gateway capabilities. |
| Eagle Enterprise | Application layer screening gateway | Implementation of Virtual Private Networking technology | Raptor Systems | Includes application-level intermediary programs for FTR, HTTP, Telnet services. Logs all server actions and warns about violations. |
| Firewall IRX Router | Screening router | DOS, MS-Windows | Livingston | Allows you to analyze the network in order to optimize network traffic, securely connect the local network with remote networks based on open networks. |
| Firewall-1 | Comprehensive firewall | Intel x86, Sun Sparc, etc. | Check Point Software Technologies | Provides protection against hacker attacks such as address-spoofing (forging packet addresses) and represents a combination network and application level protection tools. |
| Firewall-1/VPN-1 | Comprehensive firewall | Intel x86, Sun Sparc, etc. | Check Point Software Technologies | Represents the open OPSEC API application interface. Provides: — detection of computer viruses; — URL scanning; — blocking Java and ActiveX; — SMTP protocol support; — HTTP filtering; — FTP protocol processing |
| TIS Firewall Toolkit | A set of programs for creating and managing firewall systems | BSD UNIX | Trusted Information Systems | Distributed in source code, all modules are written in C. The set is intended for expert programmers. |
| Gauntlet Internet Firewall | Application layer shielding gate | UNIX, Secured BSD | Trusted Information Systems | Supports services: email, Web service, terminal services, etc. Features: encryption at the network level, protection against hacker attacks such as address-spoofing, protection against attempts to change routing. |
| FireWall/Plus | Multi-protocol firewall | Various hardware platforms | Network-1 Software and Technology | Control is implemented at the level of frames, packets, channels and applications (for each protocol). Allows you to work with more than 390 protocols, makes it possible to describe any filtering conditions for subsequent work. |
| Zastava-Jet | Comprehensive firewall | SPARC, Solaris, UNIX | Jet Infosystems | Implements the security policy: all data that does not have explicit permission — are discarded. Has a Russian certificate for the second class of protection |
As can be seen from table. 2, currently the Russian firewall market offers an extensive range of hardware and software network protection tools with a fairly wide range of technical characteristics.
Essentially, any organization choosing a firewall can find the optimal solution within the available price range and with acceptable characteristics.
Practical implementation of a modern firewall
The limitations of the journal article do not allow us to go into detail on all types of ME presented in Table 2.
Therefore, as an example, we will consider in more detail the possibilities of using the multi-protocol firewall FireWall/Plus.
The FireWall/Plus firewall is designed to solve three main tasks:
- protection of corporate network resources from attacks from the Internet;
- implementation of security measures (for a dedicated server/group of servers);
- separation of internal network segments for preventing unauthorized access attempts by an internal user.
A significant feature of this ME is the ability to work with more than 390 protocols of various levels.
Thanks to the powerful built-in filter writing language, it is possible to describe any filtering conditions.
This feature allows you to more effectively solve segment separation problems corporate network, which uses products that work with TCP/IP, IPX, DECNet protocol stacks.
The mechanism for describing application level protocols allows you to create specific schemes for limiting user access. FireWall/Plus provides protection for the Web, FTR, URLs, ActiveX and Java applications, and email.
FireWall/Plus firewall detects and combats the following attacks:
- Attacks on server authentication;
- attacks on the finger protocol (from the outside and inside);
- determining the number of the initial packet of a TCP connection;
- illegal redirects;
- attacks on DNS access;
- attacks on FTR authentication;
- unauthorized file transfer attacks;
- remote reboot attacks;
- IP address spoofing;
- MAC address spoofing;
- attacks availability (request storm);
- attacks on the server’s backup port;
- attacks using remote access servers;
- attacks on anonymous FTR access.
li>
This number of blocked attacks is determined primarily by the fact that FireWall/Plus supports three methods of network address translation: one to one; one to many; many to many.
It does not need its own IP address.
This feature makes it completely transparent on the network and virtually invulnerable to various attacks.
Features considered FireWall/Plus firewall, which is a representative of the modern generation of firewalls, show how dynamically this area of security tools is developing.
Firewall certification
Currently, the State Technical Commission of Russia has adopted the working document “Computer facilities. Firewalls.
Protection against unauthorized access to information. Indicators of security against unauthorized access to information.”
This document allows you not only to streamline the information protection requirements for firewalls, but also to compare the protective properties of products of this type.
Taking into account the prospects in the field of certification of information security means, under the leadership of the State Technical Commission of Russia, the Center for Information Security (Yubileiny, Moscow Region) organized the development of a standard methodology for conducting certification tests of firewalls.
This methodology has been tested in a number of accredited laboratories in the certification system of the State Technical Commission of Russia.
Currently, certified high-security firewalls have already appeared on the Russian market, including “Zastava-Jet” (class 2), “Zastava” and “AltaVista Firewall 97” (security class 3).
These products provide reliable protection of information resources from unauthorized access.
Conclusions
Thus, the analysis of the network protection tools presented on the Russian market, showed that currently firewalls are a fairly effective means of protecting corporate networks and their segments from external threats, as well as from unauthorized interactions of local users with external systems.
They provide high-level support for an organization's security policy with respect to all protocols in the TCP/IP family. In addition, modern firewalls are characterized by transparency for legitimate users, greater speed and high efficiency.
The main trend in the development of network protection tools is integration, in particular, firewalls with cryptographic and anti-virus means, as well as tools for analyzing the level of security.
However, along with the advantages inherent in firewalls, we should not forget that at present, although firewall is the most developed means of protection in Internet/Intranet networks, does not solve the entire complex of problems related to ensuring security in open networks.
Therefore, when solving problems related to ensuring information security, by and large, it is always necessary to use an integrated approach that includes not only technical means, but also organizational measures to protect information.